Department of Computer Science
Faculty of Physical Sciences
Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria
COSC 211 : Object Oriented Programming I - LAB02
Objectives:
To gain experience with:
- Creating objects from classes
- Fundermental Data Types
- The String class
1. Creating Objects from classes
Java is an object-oriented
programming language, meaning problems are solved by interaction among objects.
An Object is a
software-entity that models some real-world entity – e.g. A particular
rectangle, a particular student, etc.
Each object has a state
(represented by its fields) and behaviors (represented by its methods).
Objects are created from classes,
thus to create an object, we need first to design a class. We can also use classes from the Java library. The Java library consists of hundreds of
classes organized into related groups called packages.
A class is a
general blueprint or specification for a set of objects in which fields and
methods are defined.
To create an object from
a class, we use the new operator as follows:
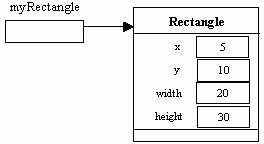
Rectangle myRectangle = new Rectangle(5,10, 20, 30);
In the above, Rectangle
is a class provided in the Java library under java.awt package. When creating a rectangle object, we need to
provide values for the top-left corner (x,y), with and height of the rectangle
object. The new operator creates the
rectangle object and returns the address of the object in memory which is then
assigned to the reference variable myRectangle.
Once an object is
created, we can call its methods using the dot operator. For example, to call the translate
method, we write:
myRectangle.translate(10,
15).
The following is a
complete program showing the above points.
Notice that if we use a Java library class that is not in the java.lang
package, we must import the class using the import statement.
Example1:
import java.awt.Rectangle; /* Creates a rectangle object, calls its translate method and then print it. */public class MoveRectangle { public static void main(String[] args) { Rectangle myRectangle=new Rectangle(5, 5, 10, 10); System.out.println("Before Translation: "+myRectangle); myRectangle.translate(15,25); System.out.println("After Translation: "+myRectangle); }} |
2. The String Class.
A string is a sequence of
characters enclosed in double quotes.
String processing is one
of the common applications of computers.
Java recognizes this fact and therefore provides special support for
string processing through a class called String in the java.lang
package, which has many useful methods.
To create a string object
from the string class we can use the new operator as follows:
String s = new String(“the content of the string in
quates”);
However, because of its
common use, Java allows strings objects to be created without using the new
operator as in:
String greeting = “Hello, World!”;
In a string object, the
characters are indexed starting from 0 as shown below:
|
greeting |
|
|||||||||||||
|
address of object |
|
H |
e |
l |
l |
o |
, |
|
W |
o |
r |
l |
d |
! |
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
The table below shows
some of the most frequently used methods of the String class:
|
method |
description |
String myString = "examples" |
int |
returns the number of characters in this String. |
int i = myString.length(); // i = 8 |
String |
returns a new String, representing the Upper-case equivalent of
this String. |
String upper=myString.toUpperCase(); // upper == "EXAMPLES" |
String |
returns a new String, representing the lower-case equivalent of
this String. |
String lower=myString.toLowerCase(); // lower == "examples" |
boolean Boolean (String s) |
returns true if the argument has the same length, and same characters as this String. the second version ignores the case. |
if (myString.equals("EXAMPLES") )// false |
int int (String s) |
returns positive number, 0, or negative number if this String is
greater than, equal to or less than the argument respectively. |
if (myString.compareTo("Yes")>0 )// true |
char |
returns the char in this String, at the index position passed to
the method. Note: Index positions always start at 0 |
char c = myString.charAt(6); // c = ‘e’ |
int int //also overloaded to accept String parameter |
finds the first / last occurrence of a character or substring
within this string, and returns the index. If the substring or char is not
found -1 is returned. |
int i = myString.indexOf("amp");// i == 2 if (myString.indexOf("Y") > 0)// returns -1 and is false |
String (int from)String (int from, int to) |
returns a part of the original String starting from the
fromIndex to the end of the string or up to but not including toIndex if one
is given. |
String s=myString.substring(5) // returns "ample" and "les" String s=myString.substring(2, 7); // returns "les" |
String |
returns a String, produced by removing any whitespace characters
from the beginning and end of this string. |
String s = “ 125 “; s = s.trim(); //returns “125” |
static String (any primitive type) |
is a static method, that is overloaded for all the primitive
data types, and returns a String representation of the argument. |
String s = String.valueOf(3.14F); // numbers to Strings "3.14" |
String concat(String s) //equivalent to + symbol |
append the argument string at the end of this string. |
String s = myString.concat(“ below”) // returns “examples below” |
Example 2:
The following
example generates a password for a student using his initials and age. (note:
do not use this for your actual passwords).
|
/* generates a password for a student using his
initials and age */ public class MakePassword {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String firstName = "Amr";
String middleName = "Samir";
String lastName = "Al-Ibrahim";
int age = 20;
//extract initials
String initials =
firstName.substring(0,1)+
middleName.substring(0,1)+ lastName.substring(3,4);
//append age
String password = initials.toLowerCase()+age;
System.out.printf("Your Password =%-20s",password);
} |
3. Assignments
|
1.
Write a program that will do the following.: (a) Declare a double variable named miles with initial value of 10.5, increase its value by 1 using the increament operator. Show the result in the form: “The current value of miles is now: ... “ (b) Declare X, Y, Z as doubles, a as an integer equal to 1, and d as a double equal to 1.0. Compute the values of the following expressions. X = d + 43 % 5 * (23 * 3 % 2), (c) Declare R and p to be doubles with p storing the value 3.758. Compute and display the value of R, where R= log p. |
|
2.
Use either Math.PI or declare PI as constant and use it below: Write a program that will display the following; "The value of exp(15) is ..." "The value of Sin 30° is: ..." "The absolute value of k is …" "The value of tan 30° is ..." where k = 2 / 4 * 4 % 3, Note also that 30° = (PI * 30)/180 radian |
|
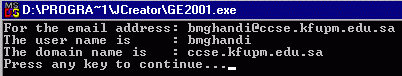
3.
Write a program that breaks a given email address
into username and domain name
|
|
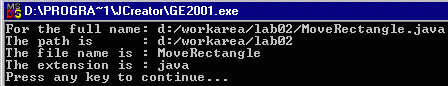
4.
Write a program that breaks a given full file
name into path, filename and extension..
|
4. Home Work
1.
The class Random of the
java.util package can be used to create an object which can then be used to
generate a random integer number from 0 to a given maximum.
Example:
Random
rand = new Random();
int
randomInt = rand.nextInt(1000);
Improve the password
example by generating a random number, multiply the random number with the age before appending it to the
initials.
2.
Write a program to
evaluate and print the value of the following mathematical function :
f(x,y) = 2x2 -
y +
3
Vary the values of x and
y according to the following table and prints the values of f(x,y) as shown in
the table.
|
x |
y |
f(x,y) |
|
3.0 |
3.0 |
|
|
2.0 |
3.0 |
|
|
-4.0 |
2.0 |
|
Very important guidelines:
- You should submit both printed
copy and soft copy in a flash drive bofore the next lab.
- All your programs files should
be saved in a folder HW1 on your flash drive.
- Code your programs according to
the Java naming conventions --
check this out on my home page.
- Indent your work so that content
of a class and methods are pushed inside by a tab or at least three
spaces.
- Use comments at the beginning of
each program to explain its purpose.
Also include your name and ID number as part of the comment.
- Use comments to explain each
variable whose purpose cannot be determined from its name.